In today’s data-driven world, the topic of data privacy has become a major concern for individuals, businesses, and governments alike. As our lives become increasingly intertwined with the digital realm, the amount of personal information being collected, shared, and stored has reached unprecedented levels. This has led to growing concerns about the potential misuse of this data and the need for robust regulations to protect our privacy.
What is Data Privacy?

Data privacy, also known as information privacy, refers to the proper handling and protection of personal data. It encompasses various aspects, including:
- Consent: Ensuring that individuals are aware of how their data is being collected and used, and providing them with the option to opt-in or opt-out.
- Notice: Informing individuals about the types of data being collected, the purpose of collection, and the parties with whom the data may be shared.
- Regulatory Obligations: Adhering to relevant laws and regulations governing data privacy, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
The Importance of Data Privacy
The importance of data privacy cannot be overstated. There are two primary drivers behind its significance:
- Data as a Valuable Asset: In the modern data economy, companies have built empires by collecting, sharing, and utilizing data. Transparency in how businesses request consent, adhere to privacy policies, and manage collected data is crucial for building trust and accountability with customers and partners.
- Individual Privacy as a Fundamental Right: Privacy is a fundamental right that allows individuals to exist freely without uninvited surveillance.
Data Privacy vs. Data Security
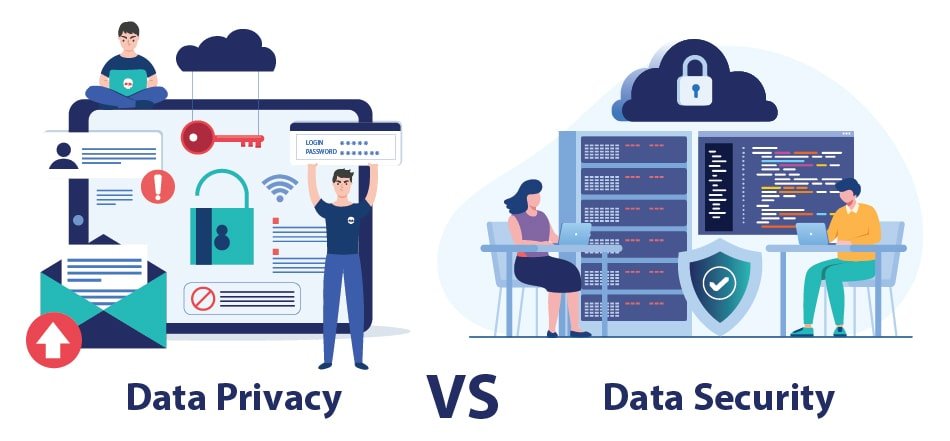
- Data Security: Protects data from unauthorized access, compromise, or theft by external attackers and malicious insiders.
- Data Privacy: Governs how data is collected, shared, and used by legal and ethical standards. Ensuring data privacy requires not only robust security measures but also adherence to regulatory requirements and ethical data-handling practices.
The Evolving Landscape of Data Privacy Regulations
Recognizing the importance of protecting personal data, governments worldwide have introduced various data privacy regulations. These laws aim to hold companies accountable and provide consumers with greater control over their personal information.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Enacted in May 2018, the GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy law that applies to all companies operating within the European Union (EU) or handling the personal data of EU citizens. It grants individuals certain rights over their data, such as the right to access, rectify, or erase their personal information. The GDPR also imposes strict obligations on companies, including the requirement to obtain explicit consent from users and implement appropriate data protection measures.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
Effective as of January 1, 2020, the CCPA is a data privacy law that applies to companies operating in the state of California or handling the personal information of California residents. Similar to the GDPR, the CCPA gives consumers the right to know what personal data is being collected about them, the right to opt out of the sale of their private details , and the right to ask for its deletion as deemed necessary.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a federal law in the United States that aims to safeguard the privacy and security of individuals’ protected health information (PHI). It sets standards for the handling and disclosure of PHI by covered entities, such as healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses.
Other Data Privacy Laws and Regulations
In addition to the GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, there are various other data privacy laws and regulations that companies must comply with, depending on their industry, location, and the types of data they handle. These include the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) for financial institutions, the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) for websites and online services targeted at children, and the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) for educational institutions.
The Challenges of Data Privacy Compliance
Complying with data privacy regulations can be a daunting task for businesses, especially those operating globally or handling large volumes of personal data. Some of the key challenges include:
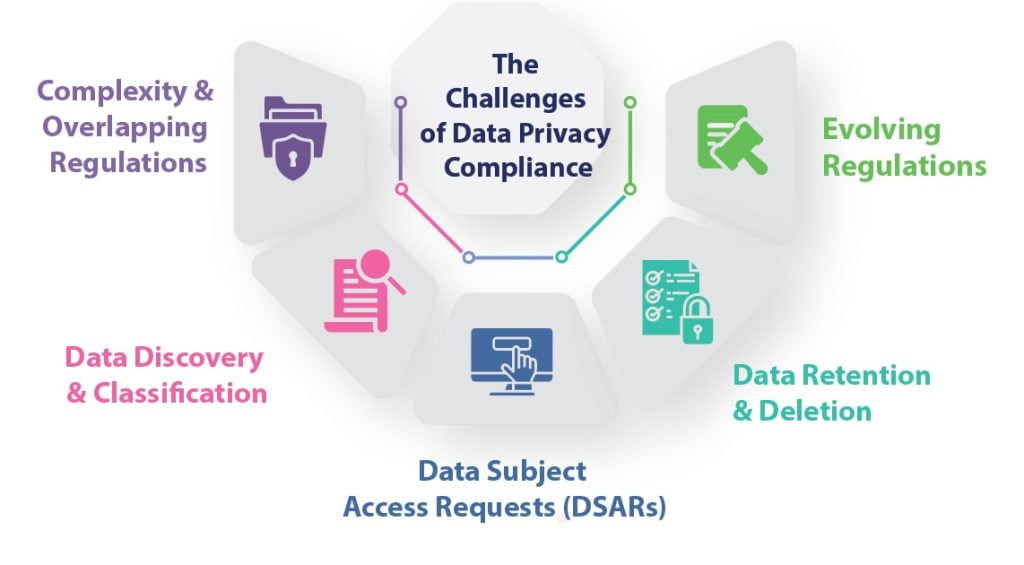
Complexity and Overlapping Regulations
With multiple data privacy laws in effect, each with its nuances and requirements, companies must navigate a complex web of regulations and ensure compliance across all jurisdictions in which they operate.
Data Discovery and Classification
Identifying and classifying personal data within an organization’s vast data repositories can be a significant challenge, particularly for companies with legacy systems and disparate data sources.
Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs)
Regulations like the GDPR and CCPA require companies to fulfill DSARs, which involve locating, retrieving, and providing individuals with copies of their data upon request. This process can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially for organizations without proper data management practices in place.
Data Retention and Deletion
Ensuring that personal data is retained only for as long as necessary and securely deleted when no longer needed is another critical aspect of data privacy compliance.
Evolving Regulations
As data privacy concerns continue to evolve, new regulations and amendments to existing laws are likely to emerge, requiring companies to stay vigilant and adapt their practices accordingly.
Data Privacy Best Practices for Businesses

To navigate the complex landscape of data privacy regulations and mitigate risks, businesses should adopt the following best practices:
Implement a Comprehensive Data Privacy Program
Develop and implement a data privacy program that addresses all aspects of data collection, processing, storage, and disposal. This program should be regularly reviewed and updated to ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Conduct Data Mapping and Classification
Identify and classify all personal data within the organization, including its sources, locations, and purposes for collection and processing. Obtain Explicit Consent: Implement mechanisms to obtain explicit consent from individuals for the collection and use of their data, and provide them with clear and accessible options to opt-out or revoke consent.
Implement Privacy by Design
Integrate data privacy principles into the design and development of products, services, and systems from the outset, rather than as an afterthought. Train Employees: Provide regular training and awareness programs to ensure that all employees understand their responsibilities regarding data privacy and handle personal data according to the organization’s policies and legal requirements.
Leverage Data Privacy Technologies
Invest in technologies and solutions that can assist with data discovery, classification, encryption, access control, and other data privacy-related tasks.
Conduct Regular Audits and Risk Assessments
Regularly audit and assess the organization’s data privacy practices, policies, and procedures to identify and address potential vulnerabilities or areas for improvement.
Establish Incident Response and Breach Notification Procedures
Develop and implement procedures for responding to data breaches or privacy incidents, including notification requirements and remediation steps.
Stay Informed and Adaptable
Continuously monitor changes in data privacy regulations and industry best practices, and be prepared to adapt the organization’s data privacy program accordingly.
Data Privacy for Consumers
While businesses bear the primary responsibility for protecting personal data, consumers can also take proactive steps to safeguard their privacy
Be Mindful of Data Sharing
Be cautious about sharing personal information online or with untrusted sources, and read privacy policies carefully before providing consent.
Use Privacy-Enhancing Technologies: Utilize tools like virtual private networks (VPNs), ad blockers, and privacy-focused browsers to protect your online activities and limit data tracking. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication: Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all accounts and services that support it, adding an extra layer of security to protect your personal information.
Review Privacy Settings
Regularly review and adjust the privacy settings on your devices, apps, and online accounts to limit the amount of personal data shared with third parties.
Exercise Your Privacy Rights: Familiarize yourself with the privacy rights granted by applicable laws, such as the right to access, delete, or opt out of the sale of your data. Stay Informed and Vigilant: Stay up-to-date with the latest privacy threats, data breaches, and best practices for protecting your personal information.
The Future of Data Privacy

As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the importance of data privacy will only grow. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain, will introduce new challenges and opportunities for data privacy.
Governments and regulatory bodies will need to adapt and update existing laws to address these new developments, while businesses must remain vigilant and proactive in their data privacy efforts. Additionally, consumer awareness and advocacy will play a crucial role in shaping the future of data privacy and holding organizations accountable.
Conclusion
In the digital age, data privacy is not just a luxury but a fundamental right and a critical business imperative. Ensuring the proper handling and protection of personal data is essential for maintaining trust, compliance, and ethical practices.
As individuals, we must be mindful of our digital footprint and exercise our privacy rights. As businesses, we must prioritize data privacy by implementing robust policies, procedures, and technologies to safeguard the personal information entrusted to us. Ultimately, data privacy is a shared responsibility that requires collaboration between individuals, organizations, and governments. By fostering a culture of privacy awareness and adhering to data protection best practices, we can navigate the complexities of the digital world while preserving our fundamental right to privacy.
Ready to unlock the potential of analytics for your digital marketing strategy? Connect with our team today by emailing us at [email protected].
All images belong to their respective owners. Please email [email protected] if removal is required.




