In October 2023, Gmail and Yahoo dropped a bomb on the email industry by announcing new sender standards that will start being enforced in February 2024. These changes primarily target high-volume senders who blast out thousands of emails per day, but they stand to impact all brands using email marketing in the future.
Why Are Big Mailbox Providers Changing the Rules?

Gmail and Yahoo provide free email services to over 1.5 billion people globally. They aim to keep the inbox safe, useful, and clutter-free, but there’s a rising tide of threats that makes achieving that goal difficult:
- Email spoofing, phishing, and scams are increasingly sophisticated thanks to AI-generated content. There was a 1265% increase in phishing attacks since late 2022.
- Some senders fail to properly authenticate emails, leaving them vulnerable to impersonation.
- Annoying marketing emails and difficulty unsubscribing frustrate users.
- Excessive spam threatens to degrade the user experience.
By enforcing proper authentication and deliverability best practices, Gmail and Yahoo will close security gaps being exploited by bad actors. Restricting shady senders also helps ensure wanted commercial email reaches the inbox.
Key Requirements for Senders in 2024

The updated mailbox provider policies aim to improve the following areas:
Email Authentication
- Use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify senders and ensure alignment between domains.
- DMARC policy must be at least p=none initially. Stricter policies may follow.
- ARC headers required to authenticate forwarded mail.
Spam Prevention
- Provide one-click unsubscribe on all marketing email.
- Keep user-reported spam complaints under 0.3%.
Infrastructure
- Have valid rDNS and PTR records for sending IP addresses.
- Use TLS encryption.
- Follow address formatting standards in RFC 5322.
The focus is on what matters most: stopping email spoofing and making it easy for recipients to disengage. But why 0.3% on reported spam? And what happens if you exceed 500 complaints per million emails? We’ll break down key stats next.
Keeping Spam Complaints Under Control

It’s logical for Gmail and Yahoo to push senders to reduce user-reported spam. Here’s why that 0.3% threshold for spam complaints matters:
- The industry average for spam complaints is around 0.1%.
- At 0.3%, you’re getting 3 complaints for every 1,000 emails sent.
- Complaint rates between 0.3% and 1% lead to bulk sender scrutiny.
- Anything over 2% causes senders to end up on blacklists.
No one wants recipients clicking “report spam” on their marketing emails. But perfectly legitimate and engaged subscribers will almost never mark you as spam.
Monitoring spam complaints shows whether your email program is healthy. If too many recipients say your mail is unwanted, something needs fixing whether that’s list quality, engagement, or overly promotional messaging.
The good news is Gmail and Yahoo won’t immediately ban senders for crossing the 0.3% spam threshold. The rules indicate temporary spikes over 0.3% are acceptable as long as the ongoing complaint rate stays under the limit most of the time.
Still, no one wants their sender reputation diminished or delivery impacted, so keeping spam complaints minimal is essential.
How Senders of All Sizes Can Prepare for 2024
If you send a few emails per month, you may wonder whether you need to worry about complex authentication protocols and spam monitoring. The answer is yes—eventually. What holds as a best practice for big senders today often becomes a requirement for smaller ones later.
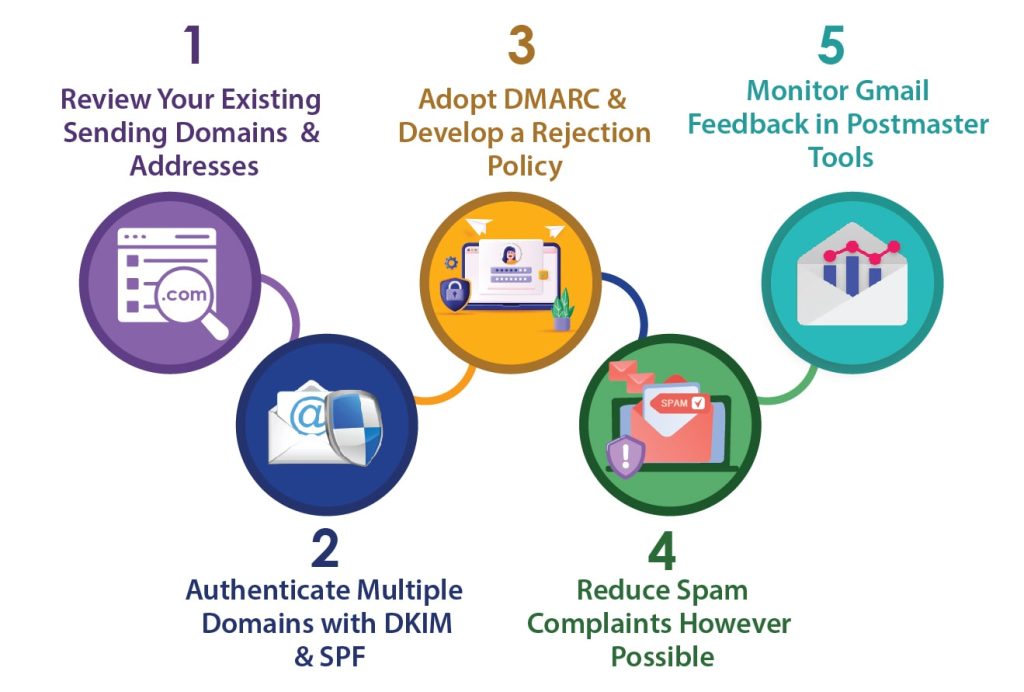
To understand what’s ahead and ensure your email program is ready, here are five steps every sender should take:
Review Your Existing Sending Domains and Addresses
The first step is knowing what domains and addresses you currently use for sending email. Check what’s set up in your email service or marketing automation platform.
Every sending domain should have a valid SPF record. But for full compliance now and in the future, properly configured DKIM and DMARC are essential additions.
For DKIM, you or your technical team will need to generate a public-private key pair and add TXT records to your DNS configuration.
With DMARC in place at p=none, you’ll start collecting delivery diagnostic data to review before deciding on a stricter policy.
Authenticate Multiple Domains with DKIM and SPF
As inbox providers validate the “From” domain along with the sending domain, it’s wise to authenticate both independently.
Set up custom DKIM and SPF records for your primary marketing domain. For transactional messages, authenticate key domains like support@ and no-reply@ in the same manner.
This ensures all sender identities align with properly authorized sending infrastructure. It also builds a positive domain reputation for sealing future deliverability.
Adopt DMARC and Develop a Rejection Policy
With domain-level DKIM and SPF established, activating DMARC is the natural next step. Start with p=none while gathering metrics on legitimate and fraudulent email traffic.
Then begin planning a ‘reject’ policy to quarantine or block unauthorized messages from people impersonating your domain. Don’t let your brand be spoofed!
As mailbox providers start requiring DMARC, getting ahead of the curve will ensure your emails keep reaching the inbox.
Reduce Spam Complaints However Possible
Confirm your email signup and preference center flows meet the one-click unsubscribe requirement. Make opting out very clear in each marketing message too.
Beyond that, revisit your subscriber engagement and list management practices. Pitch relevant offers to genuinely interested recipients who want to hear from you. Proactively prune your list by reconfirming opt-ins or removing inactive contacts.
Stay below 0.1% spam complaints and you’ll exceed new inbox provider standards with room to spare!
Monitor Gmail Feedback in Postmaster Tools
Unlike some ESPs, Google doesn’t provide third-party access to spam complaint data tracked in Gmail. However, Gmail Postmaster Tools enables you to monitor aggregated spam reports for your sending domains.
Connect your domains to Postmaster Tools for visibility into Gmail user feedback. Keep spam complaints under 0.3%, open and click-through rates healthy, and your sender reputation will remain solid.
What Happens if You Don’t Comply?
Once the February 2024 deadline passes, inbox providers will start enforcing their new policies. Here’s the likely sequence of events if senders fail to meet delivery standards:
First 30 Days
- Messages display inbox warnings about the unauthenticated sender.
- Bulk senders exceeding complaint thresholds see spam folder routing.
60 Days
- Unauthenticated mail goes to spam for most recipients.
- Temporary blacklisting of very high-complaint senders.
90+ Days
- Persistent spam folder placement.
- Possible sending blocks based on complaint levels.
The moral is avoid finding out by properly authenticating your mail now!
Long-Term Look: Where Is Email Authentication Headed?
While the DMARC requirement stops at p=none currently, it’s easy to see inbox providers pushing for stricter policies soon. As more senders implement alignment checks, why not move to quarantining failed mail? Preventing domain spoofing is crucial.
Therefore, every sender should record a reject (quarantine) or reject (block) policy in DNS today even if holding off on enforcement. That way you’re ready to deploy an aggressive policy immediately when mailbox providers demand it.
The Future of Deliverability Comes Down to Trust
At its core, the inbox is all about user trust—trust that wanted mail will arrive safely without lost legitimate messages or pesky spam. Yahoo and Gmail hope to build user confidence by ensuring all commercial senders adhere to higher privacy, security, and relevance standards.
While achieving perfect deliverability grows more complex, the keys remain unchanged: value for subscribers, care for your lists, and authenticating every link in the email chain. Do that well, and no matter what policies inbox providers dream up next, your emails will keep reaching their destination every time.
Ready to supercharge your email marketing with the latest tips? Get in touch with our team today by emailing us at [email protected].
All images belong to their respective owners. Please email [email protected] if removal is required.




