In today’s businesses, individuals responsible for overseeing various functions must handle tasks like human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and manufacturing resource planning. Managing these aspects manually can be overwhelming.

This explains the increasing popularity of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. These systems are crafted to unify all business functions, simplifying workflows and decision-making processes. This allows organizations to focus more on their core business, as the integrated system streamlines operations.
What are ERP Solutions?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions are sophisticated software platforms crafted to streamline and automate diverse business processes throughout an entire organization. These act as centralized systems, ensuring seamless data flow and information exchange across various departments, fostering efficient decision-making and resource management.
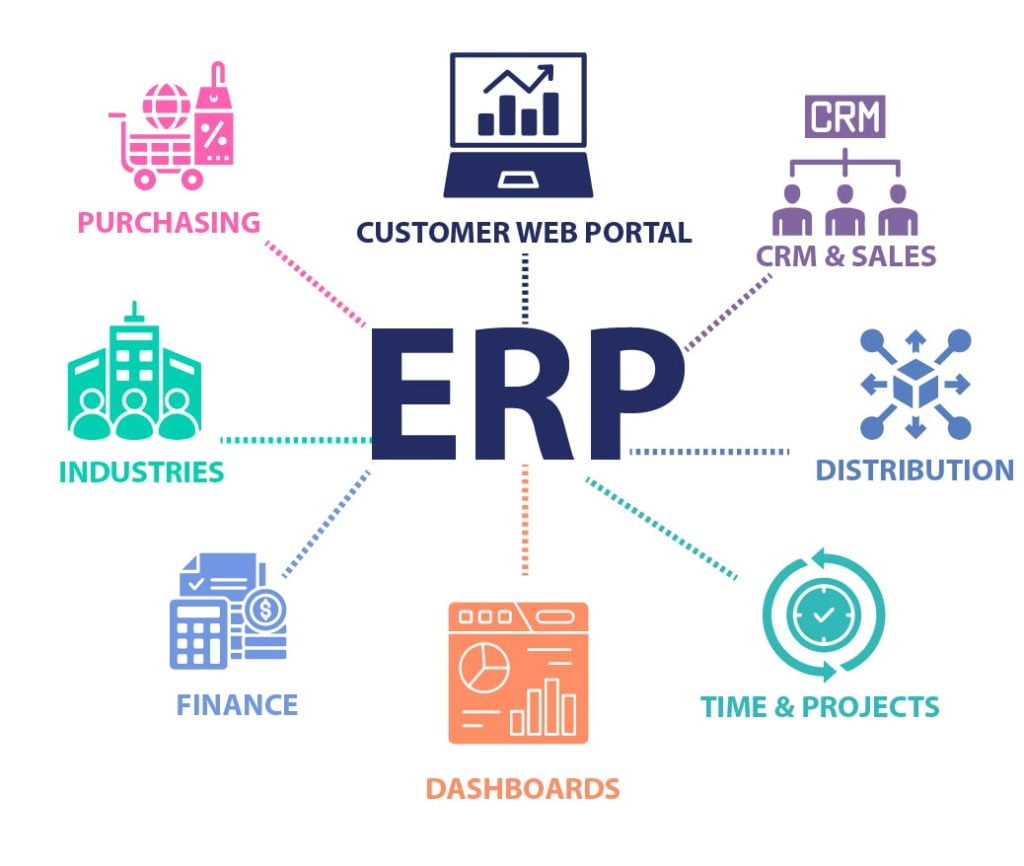
Essentially, an ERP system functions as a robust database, bringing together data from different functional areas like finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and sales. This unified database guarantees real-time access to accurate and consistent information, offering a comprehensive overview of the organization’s operations. Typically, ERP solutions consist of interconnected modules, each tailored to specific business functions.
Businesses witness significant enhancements with ERP adoption, experiencing reduced process times, improved collaboration, and centralized enterprise data. On average, an ERP system is estimated to cut operational costs by 23% and administrative costs by 22%, marking substantial savings for any business.
Key Components of ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are characterized by essential components that contribute to their effectiveness in enhancing business management. These components play a crucial role in streamlining operations and facilitating informed decision-making. Here are the key components of ERP:
Centralized Data Management
Definition: ERP systems serve as centralized repositories for organizational data.
Functionality: All departments input and retrieve data from a single database, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
Benefits: Eliminates data silos, enhances data integrity, and provides a unified view of information across the organization.
Integration of Business Processes
Definition: ERP integrates various business functions and processes into a cohesive system.
Functionality: Seamlessly connects departments like finance, human resources, supply chain, and manufacturing.
Benefits: Enhances communication and collaboration between departments, reduces redundancy, and streamlines overall business processes.
Real-Time Access to Information
Definition: ERP systems enable instant access to up-to-date information.
Functionality: Users can retrieve real-time data and reports, fostering quicker decision-making.
Benefits: Improves responsiveness to changing business conditions, enables proactive decision-making, and enhances overall agility.
These key components work in tandem to create a dynamic and interconnected system that empowers organizations to manage their operations more efficiently. Centralized data management, seamless process integration, and real-time access to information form the foundation of ERP, making it a valuable tool for businesses seeking comprehensive and responsive management solutions.
How ERP Benefits Business Management
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems provide a multitude of advantages for organizations, significantly impacting the efficiency and effectiveness of business management. Here are key ways in which ERP benefits business operations:
Streamlined Operations
- ERP systems streamline and automate various business processes, reducing manual intervention.
- Seamless integration across departments fosters better communication and collaboration.
- Elimination of duplicate data entry and processes minimizes inefficiencies.
Improved Decision-Making
- ERP systems offer real-time insights, enabling decision-makers to access accurate information promptly.
- Robust reporting and analytics tools empower organizations to make informed decisions based on comprehensive data.
- ERP supports predictive analytics, aiding in forecasting and strategic planning.
Cost Reduction Statistics
- ERP systems are estimated to reduce operational costs by an average of 23%.
- Businesses often experience a significant decrease in administrative costs, averaging around 22%.
- Efficient resource management and reduced manual efforts contribute to overall cost-effectiveness.
ERP solutions play a pivotal role in optimizing business management by streamlining operations, facilitating informed decision-making, and delivering substantial cost reductions. Adopting ERP can transform the way organizations operate, enhancing their agility and competitiveness in the ever-evolving business landscape.
Popular ERP Modules
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems consist of interconnected modules, each designed to address specific aspects of business operations. These modules work in harmony to provide a comprehensive solution for organizational management. Here are some of the popular ERP modules:
Financial Management
Functionality: Tracks financial transactions, manages budgets, and supports accounting processes.
Features: General ledger, accounts payable/receivable, financial reporting, and tax management.
Benefits: Provides real-time financial visibility, ensures compliance, and facilitates accurate financial reporting.
Inventory Control
Functionality: Manages and tracks inventory levels, orders, and stock movements.
Features: Inventory tracking, order management, demand forecasting, and warehouse management.
Benefits: Minimizes stockouts and overstock situations, improves order accuracy, and enhances overall supply chain efficiency.
Procurement
Functionality: Streamlines the procurement process, from vendor selection to purchase order management.
Features: Vendor management, purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and invoice processing.
Benefits: Optimizes procurement workflows, ensures timely deliveries, and supports strategic sourcing decisions.
Production Planning
Functionality: Plans and schedules production processes to optimize resource utilization.
Features: Production scheduling, work order management, resource allocation, and capacity planning.
Benefits: Improves production efficiency, minimizes downtime, and enhances overall manufacturing productivity.
Considerations for ERP Implementation
Implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and consideration. Here are key factors to keep in mind during ERP implementation:
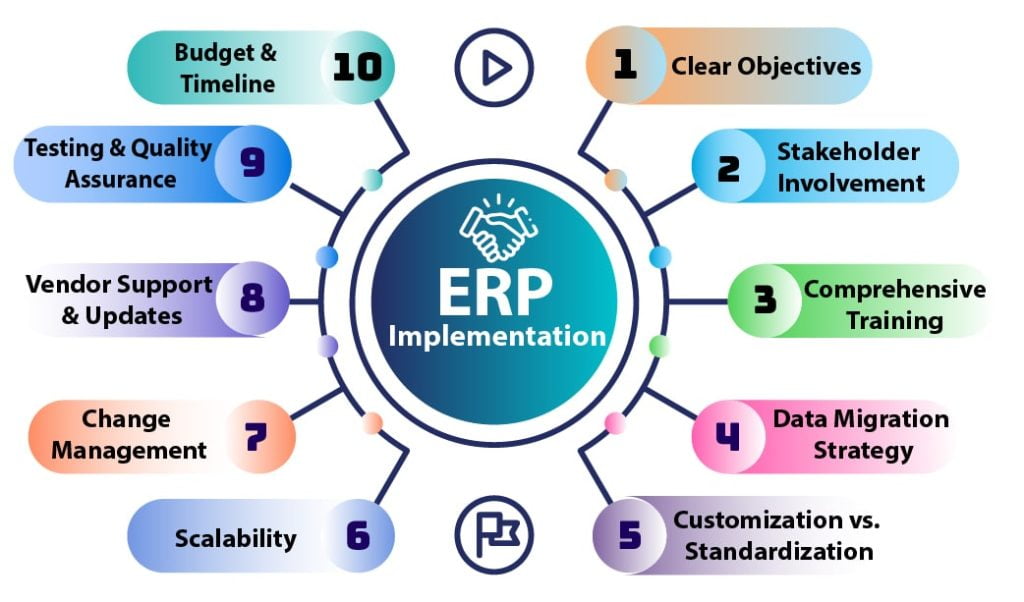
- Clear Objectives: Define clear objectives and expectations for the ERP system to align with organizational goals.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involve key stakeholders from various departments to ensure their needs and concerns are addressed.
- Comprehensive Training: Provide thorough training for end-users to ensure a smooth transition and maximize system utilization.
- Data Migration Strategy: Develop a robust strategy for migrating existing data to the new ERP system, ensuring accuracy and integrity.
- Customization vs. Standardization: Balance the need for system customization with the benefits of standardization to avoid complexity.
- Scalability: Choose an ERP solution that can scale with the growth of the organization and accommodate future needs.
- Change Management: Implement effective change management strategies to address resistance and foster a positive transition.
- Vendor Support and Updates: Ensure strong vendor support and regular updates to address issues, add new features, and maintain system security.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any issues before full implementation, ensuring system reliability.
- Budget and Timeline: Establish a realistic budget and timeline, considering potential delays and unforeseen challenges during implementation.
Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) stands as a powerful ally in modern business management, offering a holistic solution to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and achieve substantial cost savings. With key components like centralized data management, process integration, and real-time access to information, ERP systems provide a dynamic foundation for efficient organizational management.
Exploring popular ERP modules, such as Financial Management, Inventory Control, Procurement, and Production Planning, unveils the versatility and depth of these systems in addressing specific business needs. The careful consideration of factors during ERP implementation, from clear objectives and stakeholder involvement to comprehensive training and change management, is crucial for a successful integration that aligns with organizational goals.
Explore ERP solutions for your organization by visiting our website. Discover a detailed overview of how we can assist you with effective management solutions and more. Don’t hesitate to reach out – contact us today!
All images belong to their respective owners. Please email [email protected] if removal is required.




