Businesses are realizing the benefits of efficient ERP systems and are adopting them more. The market is expected to reach $60.23 billion by 2026. Advanced technology, AI, data analytics, IoT, and global competition have created a demand for transparent processes, prompting companies to invest in ERP software that can handle these features or upgrade their existing systems.
Let us know more on selecting the right deployment model for your business!
Importance of Choosing the Right Model
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are integrated software solutions designed to streamline and optimize business processes by consolidating and managing various functions across an organization. These functions typically include finance, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, and customer relationship management.

Selecting the appropriate deployment model for an ERP system is a crucial decision that directly impacts how the software is hosted, accessed, and managed within an organization. The two primary deployment models for ERP systems are Cloud-Based and On-Premise.
Cloud-based ERP
Cloud-Based ERP refers to an Enterprise Resource Planning system that is hosted on external servers and accessed through the internet. This model offers unparalleled accessibility, allowing users to connect from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for organizations with remote or globally distributed teams.

Cloud-Based ERP systems commonly adopt a pricing structure based on subscriptions. Instead of hefty upfront costs, organizations pay a recurring fee, often monthly or annually. This cost structure can be advantageous for businesses looking to manage and predict their budget more effectively.
Advantages
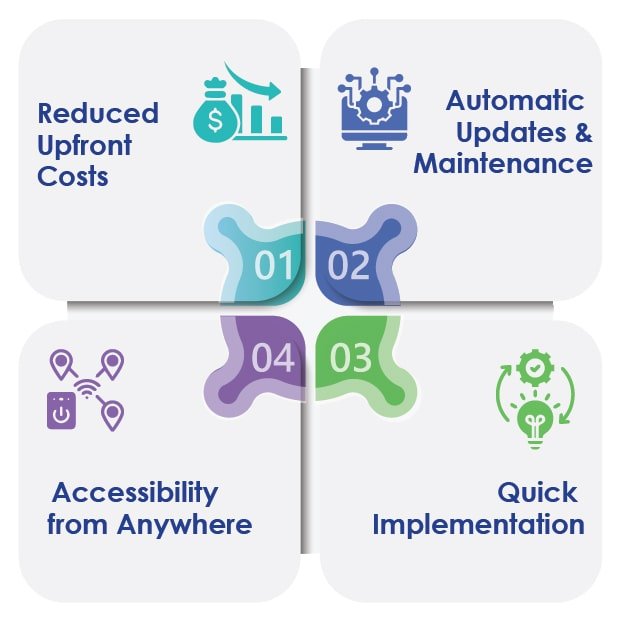
Reduced Upfront Costs
One of the primary advantages of Cloud-Based ERP is the reduced upfront costs. Organizations can avoid large initial investments in hardware and software licenses. This makes ERP technology more accessible to small and mid-sized businesses that may have budget constraints.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud-based ERP systems are managed by third-party providers who take care of updates and maintenance. This ensures that the software is always up-to-date with the latest features and security patches, relieving organizations from the burden of managing these tasks internally.
Accessibility from Anywhere
With Cloud-Based ERP, users can access the system from any location with an internet connection. This fosters collaboration among teams, facilitates remote work, and allows businesses to operate more flexibly in response to changing work environments.
Quick Implementation
Cloud-based ERP solutions often boast quicker implementation times compared to on-premise alternatives. The infrastructure is already in place, and deployment typically involves configuration rather than extensive installation processes.
Challenges
Security Concerns
Despite advancements in cloud security, some organizations remain concerned about the safety of their data in a cloud environment. Ensuring data encryption, compliance with industry standards, and selecting reputable cloud providers are essential steps in mitigating security risks.
Dependency on Internet Connectivity

Cloud-Based ERP systems heavily rely on internet connectivity. If the internet connection is disrupted, users may face difficulties accessing critical business data and applications. This dependency underscores the importance of a reliable internet infrastructure.
Limited Customization Options

Cloud-based ERP solutions often have limitations in terms of customization. Organizations may find themselves adapting to the features provided by the vendor, which could be a constraint for businesses with highly specialized or unique processes.
On-Premise ERP
On-Premise ERP refers to an Enterprise Resource Planning system that is installed and operated from the organization’s in-house servers and computing infrastructure. This model involves the organization taking full responsibility for the ERP software, hardware, and associated maintenance.

The On-Premise ERP model follows a capital expenditure (CapEx) approach. This means that organizations incur significant upfront costs for software licenses, hardware, and implementation. These costs are treated as long-term investments with the expectation of extended usage.
Advantages
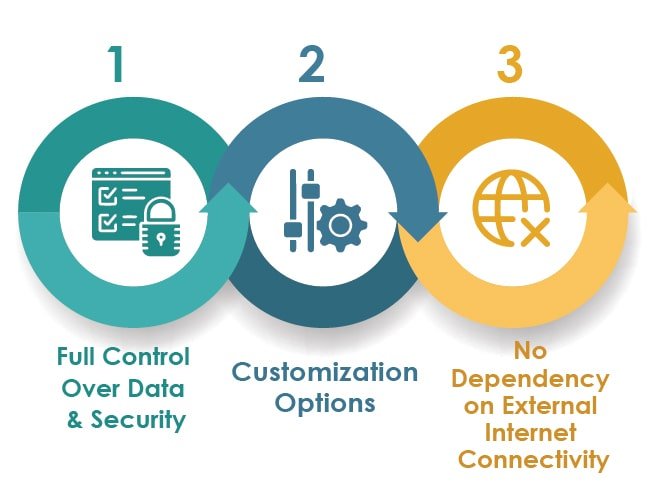
Full Control over Data and Security
One of the primary advantages of On-Premise ERP is the complete control organizations have over their data and security. Since the system is hosted internally, businesses can implement and customize security measures to meet their specific compliance and data protection requirements.
Customization Options
On-Premise ERP solutions offer high levels of customization. This is beneficial for businesses with complex processes or specific industry requirements. The ability to tailor the system allows organizations to adapt the ERP to their unique workflows, enhancing overall efficiency.
No Dependency on External Internet Connectivity
Unlike Cloud-Based ERP, On-Premise solutions do not rely on external internet connectivity for day-to-day operations. This can be advantageous for organizations operating in areas with unreliable or limited internet access, ensuring consistent access to critical business applications.
Challenges
Higher Upfront Costs

One of the significant challenges associated with On-Premise ERP is the higher upfront costs. Businesses must invest in software licenses, hardware infrastructure, and implementation services. This can be a barrier for smaller companies or those with limited initial budgets.
Longer Implementation Timelines
Implementing an On-Premise ERP system typically involves longer timelines compared to Cloud-Based solutions. This is due to the need for hardware setup, software installation, and extensive customization. The longer implementation period may delay the realization of benefits.
Maintenance and Updates Responsibility on the Business
On-Premise ERP systems require organizations to take responsibility for maintenance and updates. This includes managing software upgrades, applying patches, and ensuring that the infrastructure is kept up-to-date. This can over-burden internal IT resources.
Deciding Factors for the Right Model
Business Size and Scalability
Take into account your company’s size and its path of growth. Cloud-based ERP is often more scalable, making it suitable for growing businesses with fluctuating demands, while on-premise solutions may be better suited for larger enterprises with stable operations.
Budget Considerations
Evaluate your budget constraints and preferences. Cloud-based ERP typically involves subscription-based pricing, reducing upfront costs, whereas on-premise solutions require a substantial initial investment in licenses, hardware, and implementation.
IT Infrastructure and Expertise
Assess your organization’s existing IT infrastructure and expertise. On-premise ERP requires internal management of hardware and software, making it crucial to have skilled IT staff. Cloud-based ERP shifts infrastructure responsibility to the vendor, reducing the need for extensive in-house expertise.
Security and Compliance Requirements
Examine your industry-specific security and compliance needs. On-premise ERP provides direct control over security measures, which may be essential for highly regulated industries. Cloud-based ERP vendors often adhere to industry standards but require trust in external security measures.
Customization Needs
Determine the level of customization required for your business processes. On-premise ERP solutions offer extensive customization options, making them suitable for industries with unique workflows. Cloud-based solutions may have limitations in customization, which could impact specific business requirements.
Remote Workforce Considerations
Consider the nature of your workforce and the importance of remote access. Cloud-based ERP facilitates accessibility from anywhere, supporting a remote or globally distributed workforce. On-premise solutions may require additional measures, such as VPNs, for remote access.
Conclusion
Deciding between Cloud-Based and On-Premise ERP is a crucial step for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency and streamline operations. Our exploration highlighted the distinct features of each model, emphasizing the benefits and challenges associated with both. Cloud-Based ERP offers flexibility, reduced upfront costs, and quick implementation, making it appealing for businesses prioritizing agility. Conversely, On-Premise ERP provides full control, extensive customization, and independence from external internet connectivity, catering to organizations with specific security and operational needs.
Seeking effective digital marketing solutions to elevate your business? Your solution is just one step away. Explore the diverse range of marketing options with us by visiting our website or reaching out via email today!
All images belong to their respective owners. Please email [email protected] if removal is required.